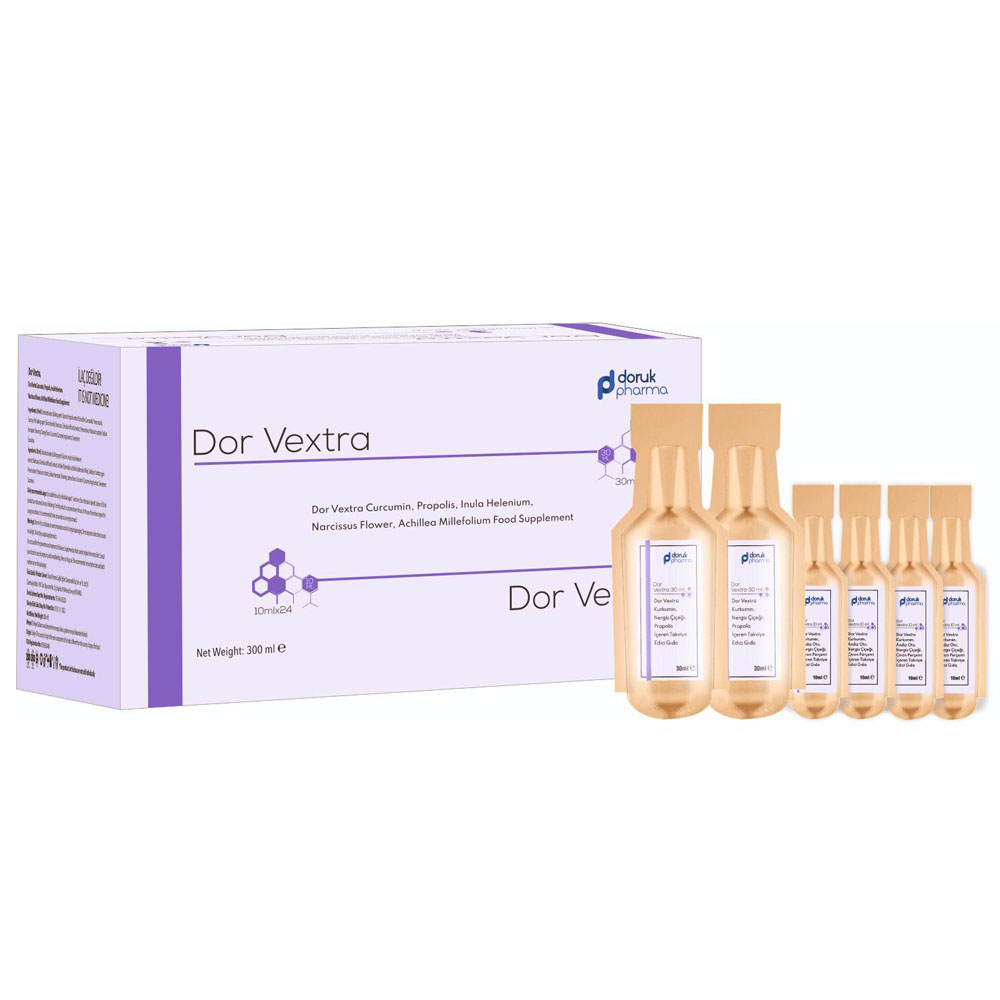
DOR VEXTRA
A Dietary Supplement Containing Curcumin, Propolis, Inula, Marigold, and Yarrow.
Ingredients (30 ml product):
Deionized Water, Volume Enhancer: Glycerin, Propolis Extract (Emulsifier: Gum Arabic, Pure Propolis, Sucrose, Anti-caking Agent: Silicon Dioxide), Marigold/Calendula (Calendula officinalis) Extract, Preservatives: Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, Flavoring: Orange Flavor, Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Extract, Sweetener: Sucralose.
Active Ingredients per Daily Intake (60 ml):
– Pure Propolis: 80 mg
– Marigold Extract: 550 mg
– Curcumin Extract: 40 mg
Ingredients (10 ml product):
Deionized Water, Volume Enhancer: Glycerin, Inula (Inula helenium) Extract, Marigold/Calendula (Calendula officinalis) Extract, Yellow Yarrow (Achillea biebersteinii Afan), Stabilizer: Xanthan Gum, Preservatives: Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, Flavoring: Lemon Flavor, Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Extract, Sweetener: Sucralose.
Active Ingredients per Daily Intake (40 ml):
– Inula Extract: 640 mg
– Marigold Extract: 440 mg
– Yarrow: 200 mg
– Curcumin Extract: 32 mg
Daily Dosage and Usage Instructions:
– Intended for individuals aged 11 and above.
– Upon opening the package, the two 30 ml products inside should be consumed at once. Every 6 hours thereafter, 10 ml should be consumed.
– When the first box is finished and the second box is started, and with every subsequent box, the same consumption pattern should be followed.
– It is recommended to consume the products on an empty stomach.
The importance of phytochemicals isolated from bioactive plants through new approaches is increasingly recognized. Plants rich in flavonoids and phenolic compounds are being used in the modern world due to their phytochemically active components. Scientific research continues successfully to support their use in product groups beneficial to humanity due to their structural diversity. Enhancing the quality of life is essential, and research on the supportive aspects of plants continues.
SECONDARY METABOLITES
These phytochemicals derived from bioactive plants are secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites are chemical compounds produced by plants as by-products of cell metabolism, although they are not essential for normal plant growth and development. While secondary metabolites are not crucial for plant survival, they are synthesized as a defense mechanism when the plant encounters stress factors. Studies show that there are over 100,000 different types of secondary metabolites. Their main categories include aliphatic, aromatic, hydroaromatic, and heterocyclic structures, which contribute to functional diversity. Research has demonstrated that complex compounds can vary from organ to organ and even between plant species, and some of these compounds are used as taxonomic markers in plant classification.
Secondary metabolites are not directly related to plant growth, photosynthesis, or product transformation processes. These compounds are synthesized through specific biosynthetic enzymes in particular tissues, organs, and developmental stages of the plant. They accumulate in high concentrations in plant organs, accounting for about 1-3% of dry weight. These secondary metabolites with pharmaceutical properties contribute to balancing billions of bacteria in the human gastrointestinal system, classified under approximately 1,000 species.
CURCUMIN EXTRACT (CURCUMA LONGA)
Commonly known as Turmeric, Curcumin is a yellow-orange phenolic compound isolated from the turmeric (Curcuma longa) plant, widely used in Asian countries as a spice. Traditionally used in various applications, Curcumin consists of curcumin (diferuloylmethane), demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, extracted from the root of the Curcuma longa plant. Besides curcuminoids, the plant also contains volatile oils (turmerone, atlantone, and zingiberene), sugars, proteins, and resins. It has a high methoxylation level and a low hydrogenation level in its chemical structure. JECFA and EFSA have classified it as a safe phytochemical.
PROPOLIS
Bees collect resin from plant shoots, branches, and trunks, mixing it with honey, beeswax, pollen, and throat enzymes in different compositions. In other words, bees collect resin, store it in pollen baskets on their hind legs, and transport it to the hive. Propolis is used for coating and sterilizing larval cells, sealing hive cracks, reducing hive entrance holes, stabilizing frames, and mummifying large intruders that cannot be removed from the hive. The primary purpose of bees producing propolis is to use it as an antiseptic to protect the hive from microbial infections and unwanted guests. Analyses have identified over 300 compounds in propolis, including phenolic compounds, aromatic acids, volatile oils, beeswax, and amino acids. The main bioactive components of propolis are flavonoids and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. Propolis composition varies depending on the plant source, typically containing 50% resinous compounds and balsam, 30% beeswax, 10% aromatic oils, and 5% bee pollen, with the remaining 5% consisting of flavonoids, amino acids, and vitamins.
MARIGOLD EXTRACT (CALENDULA OFFICINALIS)
Contains carotenoids, flavonoids, phenolic acids, glycosides, steroids, sterol quinones, volatile oils, proteins, amino acids, lipids, vitamins, and minerals with pharmaceutical effects. Due to its water-soluble polycarbon structure, it can reach tissues easily. The Calendula officinalis plant holds significant importance among medicinal plants and is used in pharmacology, food, ornamental, and cosmetic industries. Recent studies show its growing applications. Also known as pot marigold, this annual herbaceous plant grows 20-60 cm tall, with bright yellow-orange flowers blooming between April and November. Its flowers are actively utilized.
INULA EXTRACT (INULA HELENIUM)
Its pharmaceutical effects are attributed to flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolic compounds. Its chemical composition contains bioactive sesquiterpene lactones. Belonging to the Asteraceae family, this perennial medicinal plant is used in various applications worldwide.
YARROW (ACHILLEA BIEBERSTEINII)
Contains phenolic and flavonoid compounds. Known as Yarrow, its structure includes achilleine, apigenin, azulene, camphor, coumarin, inulin, menthol, quercetin, rutin, and salicylic acid. Yarrow is one of the oldest and most widely used medicinal plants.
References
– Alaca, F. & Arslan, N. (2012). The Importance of Secondary Metabolites in Plants. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, Issue: 358.
– Bakır, Ö. (2020). Secondary Metabolites and Their Roles. UAZİMDER International Journal of Anatolian Agricultural Engineering Sciences, 2(4):39-45.
– Spiridon et al. (2013). Antioxidant and Chemical Properties of Inula helenium Root Extracts. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 11(10), 1699-1709.
– Twain & Hasan (2022). Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from Plant Sources: Types, Synthesis, and Their Therapeutic Use. Int. J. Plant Biol., 13:4–14.
– Yuan et al. (2021). The Role of Bioactive Compounds in Natural Products Extracted from Plants in Cancer Treatment and Their Mechanisms Related to…




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.